
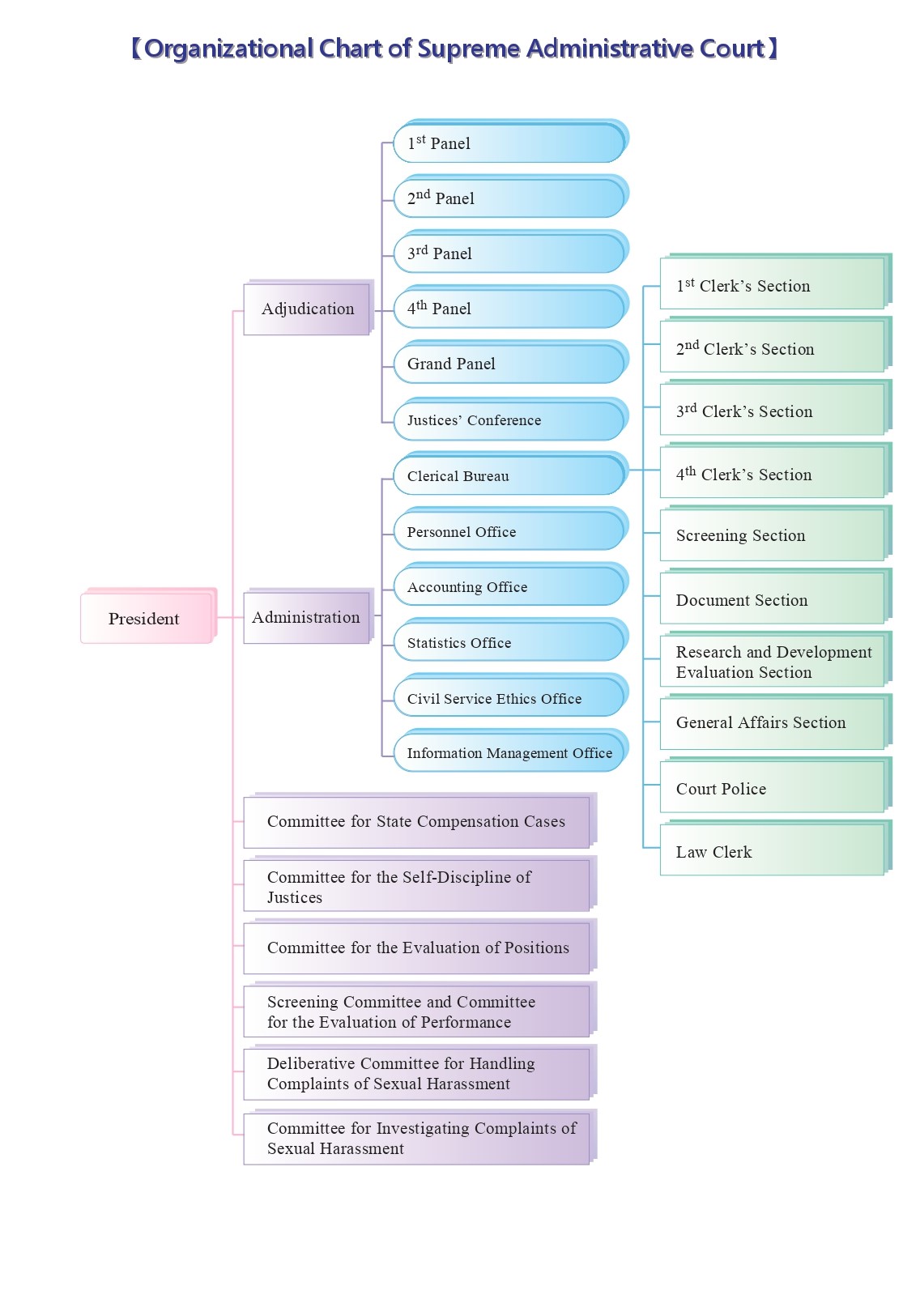
Organization
1. President
This Court has a President of the rank of special appointment, who is in charge of all of the Court’s administrative affairs, serves as a Justice himself or herself, and serves as the Presiding Justice of the Grand Panel.
2. Adjudication
(1) Panels
Each panel, comprised of a Presiding Justice and four Associate Justices, decides cases by majority. There was only one panel in 1949, but there are four panels now owing to the increasing caseload.
(2) Grand Panel or da fa tin
The Grand Panel, consisting of nine justices, adjudicates the issues proposed by a panel of this Court, and makes a ruling (ts’ai ting) that bind the proposing panel on the adjudication of the case or matter in question. The President serves as the Presiding Justice of the Grand Panel. The proposing panel appoints one member for the Grand Panel. Justices’ Conference elects by vote the other seven members for the Grand Panel.
(3) Justices’ Conference
Justices’ Conference, chaired by the President, is attended by all current justices of this Court. Justices’ Conference decides on the assignment of judicial functions among justices, and advises the President on the evaluation of justices, the disciplinary matters against justices pursuant to Article 21 of the Judges’ Act, and other things that may significantly affect justices.
3. Committees
(1) Committee for State Compensation Cases
In order to handle state compensation cases claimed by individuals in accordance with the State Compensation Law, Supreme Administrative Court Regulations on the Handling of State Compensation Cases prescribes a five- member Committee for State Compensation Cases, dealing with the investigation, negotiation, litigation, and claims of state compensation cases.
(2) Committee for the Self-Discipline of Justices
Pursuant to the Court Regulations for the Self-Discipline of Judges and Justices at All Levels, this Court has a Committee for the Self-Discipline of Justices, dealing with matters relating to the self-discipline of Justices in order to preserve the integrity, professional ethics and reputation of justices.
(3) Committee for the Evaluation of Positions
Pursuant to the Regulations Governing the Evaluation of Positions, the court has a Committee for the Evaluation of Positions which is responsible for the preliminary evaluation of the position of judges by examining the actual facts based on the principle of fairness and justice.
(4) Screening Committee and Committee for the Evaluation of Performance
Pursuant to the Civil Servant Promotion Act and its implementing regulations and the Civil Servant Performance Evaluation Act, this Court sets up the Screening Committee and the Committee for the Evaluation of Performance to make annual merit rating, special merit rating, and the preliminary regular assessments of the staff for rewards or disciplines in an open, fair, and just manner, balancing the principles of internal promotion and external hiring.
(5) Deliberative Committee for Handling Complaints of Sexual Harassment
Pursuant to the Act on Gender Equality at Work, and this Court’s Regulations on Preventing, Complaining about, and Handling of Sexual Harassment at Work, this Court sets up the Deliberative Committee for Handling Complaints of Sexual Harassment in order to prevent sexual harassment and provide a safe work environment.
(6) Committee for Investigating Complaints of Sexual Harassment
Pursuant to the Act on the Prevention of Sexual Harassment, and this Court’s Regulations on Preventing, Complaining about, and Handling of Sexual Harassment at Work, this Court sets up the Committee for Investigating Complaints of Sexual Harassment in order to prevent sexual harassment and protect the rights and interest of victims.
4. Administration
Administrative matters of this Court are dealt with by Clerical Bureau, Personnel Office, Accounting Office, Statistics Office, Civil Service Ethics Office, and Information Management Office respectively under the supervision of the President. The Chief Clerk, the head of the Clerical Bureau, is responsible for conducting administrative affairs on the orders of the President, as well as overseeing all work within the Clerical Bureau. The Clerical Bureau consists of subordinate Sections, such as Clerk’s Sections, Screening Section, Document Section, Research and Development Evaluation Section, and General Affairs Section. Each Section is led by a director. Also working in the Clerical Bureau are several court police and law clerks.
- Release Date:2021-04-25
- Update:2024-03-08
